Fleas and ticks can cause serious diseases that affect humans, as well as their pets. These diseases can result in long-term complications or even death if left untreated. To reduce your risk of contracting these illnesses, control fleas and ticks in your home and learn more about the diseases listed below.
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease occurs when ticks infected with the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium bite humans,

Female Adult Deer Tick
dogs, and cats. Though pets with the disease cannot infect humans, their owners can become infected if they are bitten by ticks that reside on their pets’ bodies.
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the disease is most often transmitted to humans through the bite of a type of tick called the blacklegged tick. In order for the infection to occur, the tick will need to latch on to the body of its human host for at least 36 hours. If the tick remains attached to one’s body for this period of time and is able to transmit the disease, serious symptoms of Lyme disease will soon follow.
Symptoms include fever, fatigue, headaches, rash, swollen joints, facial palsy, arthritis and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
To prevent Lyme disease transmission, homeowners should learn how to control a tick infestation. Also, use the correct technique to remove ticks if you or your pet is bitten.
Plague
Plague is a serious disease that affects humans due to a bacterium called Yersinia pestis. This disease occurs when fleas carrying this bacterium bite humans and animals. These fleas usually get infected by rodents, so homeowners should be vigilant in controlling rat populations in their home.
The disease causes lymph nodes to become tender and swollen. Other symptoms include fever, chills, headaches, and extreme weakness. If left untreated, plague can cause serious medical complications or death.
Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is a bacterial disease transmitted by the infected lone star tick. This disease usually occurs within the eastern and southcentral United States and may result in symptoms that include fever, fatigue, and headaches.
Persons most likely to contract this disease include those that have compromised immune systems, for example, those with cancer or HIV infection. Treatment of Ehrlichiosis usually involves the use of antibiotics.
Individuals can reduce their risk of getting this disease through tick control within their homes, as well as surrounding woodlands.
Tapeworm Infection
Tapeworm Infection, also known as Dipylidium, affects dogs, cats, and in rare cases humans. Pets become infected when they swallow a flea that is infected with the larvae of a tapeworm. This may occur when they scratch a spot infested with fleas or simply groom themselves.
Once your pet or individual swallows these fleas, the tapeworm larvae will travel to the intestines where it will reside and eventually grow into several adult tapeworms. Tapeworm infection can lead to weight loss or irritation around the anus.
Treatment for this disease in both humans and pets involves the use of medication which dissolves tapeworm within the intestines. Prevention of tapeworm infection begins when homeowners control flea infestation.
Rocky mountain spotted fever
This is a tick-borne disease that affects humans when they are bitten by ticks that are infected with a bacterium
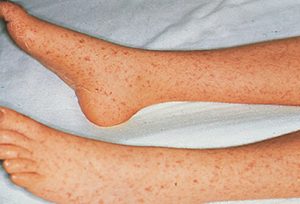
Early symptoms of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
called Rickettsia rickettsii. Rocky mountain spotted fever can lead to death if not treated in the early days of the disease when the symptoms begin. Symptoms include rash, fever, abdominal pain, vomiting, and muscle pain.
To prevent the chances of becoming infected with this disease, protect your dogs or other pets from ticks. Also, avoid woodlands or bushy areas that have high grass or many fallen leaves as these are areas in which ticks often flourish.
If you cannot avoid these areas wear repellents that contain DEET or clothing that has been treated with Permethrin. Also prevent bites by wearing long-sleeved garments.
Cat Scratch Fever
Cat Scratch Fever results from the Bartonella henselae bacterium. Cats get infected through flea bites or droppings. They pass on this bacterium when they scratch or bite humans or when they lick a person’s open wound. This can result in the scratch or bite becoming swollen and red, sometimes containing pus. The disease may also cause an infected person’s lymph nodes to swell or become painful, loss of appetite, headaches and fever
To prevent Cat Scratch Fever, wash cat scratches or bites with soap and running water. Also, wash your hands after playing with cats. Control fleas on your cat and be sure to keep your cat’s nails trimmed. You may also consider hiring a pest control expert to treat serious cases of flea infestation.

No Comments